Know about Hair, its problems and treatments!
Every mammal has hairs all over the body. Hair is made up of a long chain of tough proteins known as Keratin. It grows from hair follicles (a dynamic organ found in mammalian skin, resides in the dermal layer of the skin and is made up of 20 different cell types) which is found in dermis (The dermis or corium is a layer of skin between the epidermis (with which it makes up the cutis) and subcutaneous tissues).
Apart from areas of glabrous skin (no hair area or bald or hairless area), In the human body, hair follicles produce two types of hair as thick hair aka Terminal (they are thick, long, and dark and are found in armpit, face, chest, abdominal, leg, arm, and foot areas) and thin hair aka Vellus Hair (these are short, thin, slight-colored, and hardly noticeable thin hair that develops on most of a person’s body during childhood and are found in lips, the back of the ear, the palm of the hand, the sole of the foot, some external genital areas, the navel and scar tissue).
Internal anatomy of Hair:
The hair has two distinctive parts as hair follicles (Inside part of the skin) and hair shaft (Outside part of skin).
Hair Follicle: A hair follicle develops each hair in the skin. The hair bulb develops the base part of the hair follicle. The living cells or stem cells divide and grow to create hair shaft. The nourishment of the cells in hair bulb is happen only by blood vessels. These blood vessels supply hormones to hair bulb that modify hair growth and structure at different times of life.
Hair shaft: The shaft is the rigid filamentous part that extends above the skin surface. A cross section of the hair shaft may be divided roughly into three zones such as cuticle (several layers of flat and thin cells), cortex (the keratin bundles in cell structures) and medulla (disorganized and open area at the fiber’s center).
Each strand of hair is made up of the medulla, cortex, and cuticle. The Medulla is the inner most layer, it may be absent (specially in fine or light blonde hair). The Cortex is middle part which provides strength, moisture, colour and texture. The cuticle is outer covering as scales which protects cortex part. The cortex comprises melanin, which colors the fiber which is based on the number, distribution and types of melanin granules. The shape of the follicle determines the shape of the cortex, and the shape of the fiber is related to how straight or curly the hair is. People with straight hair have round hair fibers. Oval and other shaped fibers are generally wavy or curly. The cuticle is the outer side covering.
The diameter of human hair differs from 0.017 to 0.18 millimeters (0.00067 to 0.00709 in). Hair functional activities as there are a lot of small, tubular glands and sweat glands that produce watery fluids that cool the body by evaporation. The glands at the opening of the hair which produce a fatty secretion that lubricates the hair.
The living part of the hair is found in follicle. The hair is always grown in hair follicle, while the visible part of the hair is hair shaft which has no activity and known as dead part of the hair.
Natural colour of Hair:
The hair gets colour due to the two types of hair pigments. These pigments are melanin types and produced inside the hair follicle and packed into granules found in the fibers. Eumelanin is the main pigment in brown hair and black hair, while pheomelanin pigment gives red colour in hair. Blond hair is the result of having minute pigmentation in the hair strand. Gray hair occurs when melanin production drops or stops.
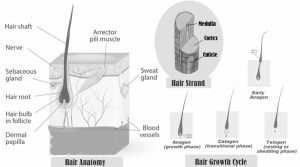
Growth cycle of Hair:
Hair growth is divided in three phases as Anagen, Catagen and Telogen.
Each strand of hair on the human body is at its own stage of growth. Once the cycle is complete, it restarts and a new strand of hair starts to build. The rate or speed of hair growth is about 1.25 centimetres or 0.5 inches per month, or about 15 centimetres or 6 inches per year.
Anagen (growth phase): Each hair spends several years in this phase. The anagen phase is identified as the growth phase. This is the phase where the hair physically grows approximately 1 cm per month. It begins in the papilla and can last from two to six years. The longer the hair stays in the anagen phase, the longer it will grow. During this phase, the cells in the papilla divide to produce new hair fibers. 85% – 90% of the hairs on one’s head are in the anagen phase at any given time.
Catagen (transitional phase): Over a few weeks, hair growth slows and the hair follicle shrinks. The catagen phase, also identified as the transitional phase, allows the follicle to, in a sense, renew itself. During this period, which continues about two weeks, the hair follicle shrinks due to disintegration and the papilla detaches and cutting the hair strand off from its nourishing blood supply. Signals sent out by the body (that only selectively affect 1 percent of all hair of one’s body at any given time) determine when the anagen phase ends and the catagen phase begins.
Telogen (resting or shedding phase): Throughout the telogen or resting phase (also known as shedding phase) the follicle remains latent for one to four months. Over months, hair growth stops and the old hair detaches from the hair follicle. A new hair begins the growth phase, pushing the old hair out. Ten to fifteen percent of the hairs on one’s head are in this phase of growth at any given time. The follicle will begin to grow again, softening the anchor point of the shaft initially. The hair base will break free from the root and the hair will be shed. Within two weeks the new hair shaft will begin to arise once the telogen phase is complete. The process results in normal hair loss known as shedding.
Hair Conditions or Hair loss related issues:
There are a lot of types issues regarding hair fall in human being. It may genetically, some deficiencies, food habits, infections and hormonal imbalance etc.
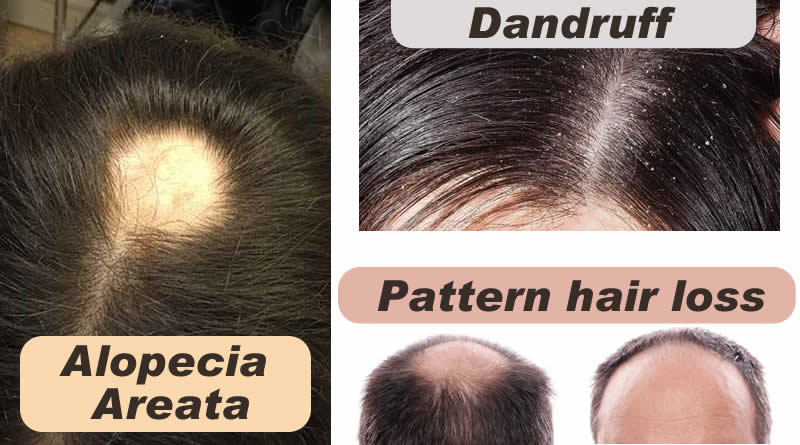
Alopecia areata: Alopecia areata or spot baldness which is a condition in which hair is lost from some or all areas of the body. This cause a coin size bald spots are found on the scalp. Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disease. Risk factors include a family history of the condition and Psychological stress. The underlying mechanism involves failure by the body to recognize its own cells with subsequent immune mediated destruction of the hair follicle. There is no cure for the condition. Efforts may be used to try to speed hair regrowth such as cortisone injections. The main cause of alopecia is unknown; the hair usually grows back.
Pattern hair loss: The most common type of hair loss in men and female. Pattern hair loss, known as male-pattern hair loss when it affects males and female-pattern hair loss when it affects females, is hair loss that mainly affects the top and front of the scalp. In males the hair loss often identifies as a receding hairline while in females it characteristically presents as a thinning of the hair. The reason behind the Male pattern hair loss is believed to be due to a combination of genetics and the male hormone dihydrotestosterone. The cause in female pattern hair loss remains undistinguishable. Pattern hair loss by the age of 50 affects about half of males and a quarter of females. It is the most common factor of hair loss. For this, treatments may include minoxidil, finasteride, or hair transplant surgery.
Dandruff (seborrheic dermatitis): Dandruff is a skin condition that largely affects the scalp. Due to mild inflammation of the scalp, resulting in scaly skin that may be itchy and flake off. A more severe form of the condition, which includes inflammation of the skin, is known as seborrheic dermatitis and it may also affect the ears and face. The reason of Dandruff is unclear but believed to contain a number of genetic and environmental factors. It involves the over growth of skin cells. The usual treatment is with antifungal cream such as ketoconazole. Males are more frequently infected than females.
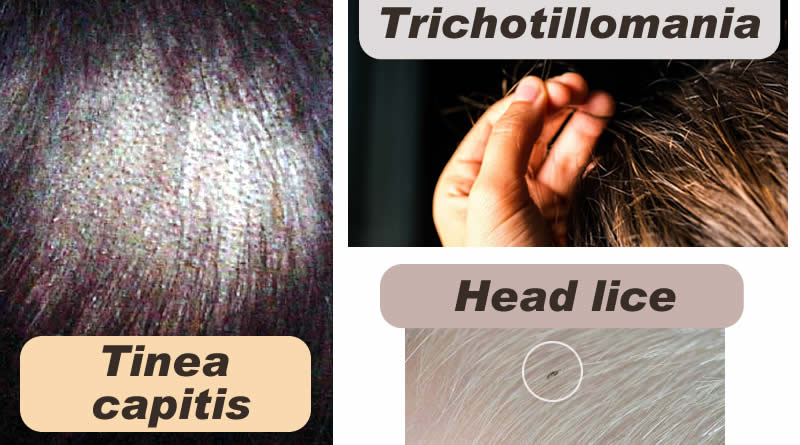
Tinea capitis (ringworm): Tinea capitis (aka herpes tonsurans or ringworm of the hair or ringworm of the scalp or scalp ringworm or tinea tonsurans) is a cutaneous fungal infection (dermatophytosis) of the scalp. It creates round patches of hair loss. Although the patches can appear in a ring shape. The disease is mainly caused by dermatophytes in the Trichophyton and Microsporum genera that invade the hair shaft. It is single or multiple patches of hair loss, sometimes with a ‘black dot’ pattern (often with broken-off hairs), that may be accompanied by inflammation, scaling, pustules, and itching. The treatment of choice by dermatologists is a safe and low-cost oral medication, griseofulvin, a secondary metabolite of the fungus Penicillium griseofulvin.
Trichotillomania: It is also known as hair pulling disorder which is an impulse control disorder characterised by a long term urge that results in the pulling out of one’s hair. A mental disorder that includes the tempting urge to pull out one’s hair. The hair pulling results in patches of noticeable hair loss. Its cause is unknown. Hair removal may occur anyplace; but, the head and around the eyes are most common. It occurs more frequently in those with obsessive compulsive disorder. Episodes of pulling may be caused by anxiety. It is also possible due to body dysmorphic disorder (remove hair for good look). Treatment is normally with cognitive behavioral therapy. The medicine clomipramine may also be helpful. Trichotillomania is generally to affect one to four percent of people.
Head lice: Head lice are wingless insects spending their entire lives on the human scalp and feeding exclusively on human blood. Preschool and elementary school-aged children and adults who live with children are most vulnerable to catching head lice, which are only spread through close contact. Humans are the only known hosts of this specific parasite. It may become a reason for hair loss and transmission of dangerous diseases.
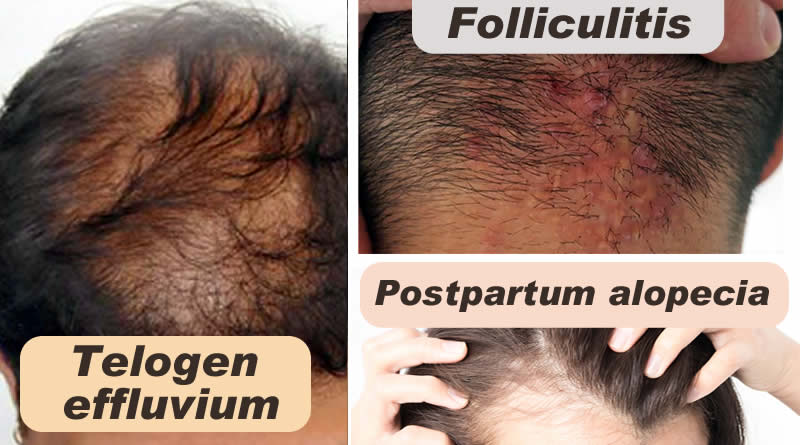
Telogen effluvium: Telogen effluvium is a scalp disorder characterized by the thinning or shedding of hair resulting from the early entry of hair in the telogen phase (the resting phase of the hair follicle). Emotional or physiological stress may result in a modification of the normal hair cycle and cause the disorder. Its potential reasons containing eating disorders, fever, childbirth, chronic illness, major surgery, anemia, severe emotional disorders, crash diets, hypothyroidism, and drugs. In this condition, hair can abruptly fall out in large patches. Vitamin D levels can also play a role in normal hair cycle.
Postpartum alopecia: Hair loss often follows childbirth without causing baldness. Hair loss after delivering a baby- is a form of telogen effluvium and generally resolves without treatment.
Folliculitis: Folliculitis is the infection and inflammation of one or more hair follicles. The condition may occur anywhere on the skin except the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. The rash may appear as pimples that come to white tips on the face, chest, back, arms, legs, buttocks, or head. Inflammation of hair follicles, generally due to an infection. Staphylococcus aureus is bacteria that normally causes folliculitis. Acne is a form of folliculitis that is caused by inflammation. This inflammation can sometimes be worsened by the bacteria Propionibacterium acnes. Folliculitis can affect people of all ages.
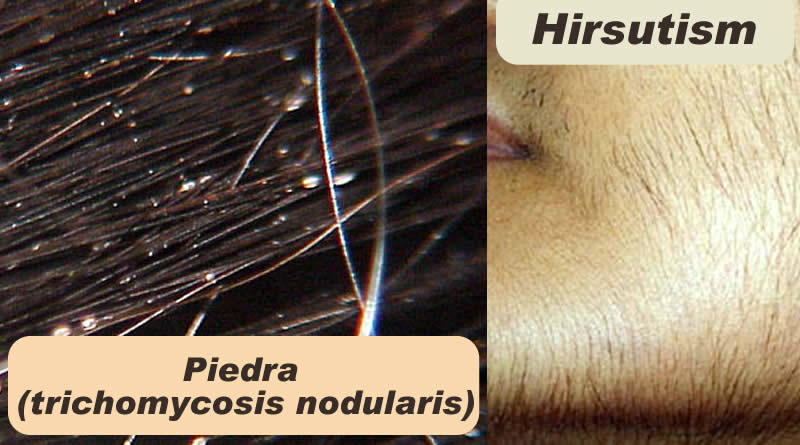
Piedra (trichomycosis nodularis): Piedra is a hair disease caused by a fungus. Fungal infection of the hair shaft. White piedra (or tinea blanca) is a fungal infection (mycosis) of the hair which is caused by several species of fungi in the genus Trichosporon. Black piedra is a form of piedra caused by Piedraia hortae. Hard nodules made of fungus cling to hair fibers, sometimes causing hair loss.
Hirsutism: Hirsutism is excessive body hair in men and women on parts of the body where hair is normally absent or minimal, such as on the chin or chest in particular, or the face or body in general. A condition in which women develop male-pattern hair (such as facial hair). Hirsutism affects members of either sex, since rising androgen levels can cause excessive body hair, particularly in locations where women normally do not develop terminal hair during puberty (chest, abdomen, back, and face). The medical term for excessive hair growth that affects any gender is hypertrichosis. Hirsutism can be caused by either an increased level of androgens, the male hormones, or an oversensitivity of hair follicles to androgens. Male hormones such as testosterone stimulate hair growth, increase size and intensify the growth and pigmentation of hair. Other symptoms associated with a high level of male hormones include acne, deepening of the voice, and increased muscle mass. The condition is called hyperandrogenism. An excess of testosterone due to a medical condition is usually responsible.
Hair use in forensic, drug and toxic exposure tests:

Hair DNA testing is used for establish paternity or as evidence in a crime investigation. Hair follicles contain DNA which is the base for testing. Drugs related test is also carried out with the help of hair. A sample of hair can be tested for recent drug use. Testing of hair for toxic exposures, such as lead or mercury poisoning
Different methods of Hair Treatments:
Minoxidil (Rogaine): Minoxidil is an antihypertensive vasodilator medication and is used to treat hair loss. It is applied to the scalp, which can help prevent hair loss in most people when used daily. It is available as a generic medication for the treatment of androgenic alopecia.
Finasteride (Propecia): A medicine for men taken in pill form daily, which regrows some hair and prevents hair loss in most men who use it. Finasteride’s brand names are Proscar and Propecia which is used chiefly to treat scalp hair loss in men. It can also be used to treat unnecessary hair growth in women. It is taken by mouth.
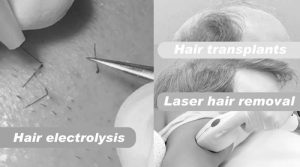
Hair transplants technique: It is a surgical technique that removes hair follicles from one part of the body, called the ‘donor site’ and placed at bald or balding part of the body known as the ‘recipient site’. The technique is primarily used to treat male pattern baldness. In this minimally invasive procedure, grafts containing hair follicles that are genetically resistant to balding, (like the back of the head) are transplanted to the bald scalp. Hair transplantation can also be used to restore eyelashes, eyebrows, beard hair, chest hair, pubic hair and to fill in scars caused by accidents or surgery such as face-lifts and previous hair transplants. Surgery to remove skin and hair from the back of the scalp, and transplant groups of hair follicles to areas of thin hair.
Hair electrolysis technique: Hair removal’s procedure to permanently remove human hair from the body. Electrolysis is the authentic process of removing hair using electricity. A very fine needle is inserted into a hair follicle, and electrical current is applied. The electricity destroys the follicle, preventing hair growth.
Laser hair removal technique: Laser hair removal is the process of hair removal by means of exposure to pulses of laser light that destroy the hair follicle. A laser is aimed at the cells in the hair follicle, and the laser’s high energy destroys cells there, preventing hair growth.
Credit: Anushri Sanjeevani